Visual Studio Code
DevSpace allows easy Visual Studio Code integration through Visual Studio's Remote - SSH Extension. The idea is to use DevSpace to setup an SSH connection to a Kubernetes container and then open Visual Studio Code directly inside that development container.
Unfortunately, Visual Studio Code is not supporting any alpine based images as of now, so be sure to use a non-alpine based image for starting Visual Studio Code.
Prerequisites
The following components need to be installed before you can use DevSpace with Visual Studio Code:
- DevSpace
- A Kubernetes cluster either locally (e.g. Docker Desktop, Rancher Desktop, minikube etc.) or in a Cloud Environment (e.g. GKE, AKS, EKS etc.) and a valid Kubernetes context configured locally.
- Visual Studio Code
- Remote - SSH Extension for Visual Studio Code
- Visual Studio Code - Command Line Interface
TL;DR
Run the following commands in a terminal
# Clone the example project
git clone https://github.com/loft-sh/devspace-vscode-example.git
# Switch to the folder
cd devspace-vscode-example
# Open Visual Studio Code in a Container
devspace dev -n my-namespace
1. Clone the example Project
We have prepared a small example Golang project that shows how you can use DevSpace and Visual Studio Code together. To checkout the example project run:
# Clone the example project
git clone https://github.com/loft-sh/devspace-vscode-example.git
# Switch to the folder
cd devspace-vscode-example
The example project deploys a small pod with the golang:1.18 container, syncs our source code into the container and then opens Visual Studio Code inside that container. Before we run DevSpace let's take a look at the application. Open main.go:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello World!")
}
func main() {
fmt.Println("Started server on :9000")
http.HandleFunc("/", handler)
http.ListenAndServe(":9000", nil)
}
It's a simple web server that runs on port 9000 and returns a Hello World! message.
2. Configure DevSpace
Let's take a look at the devspace.yaml:
version: v2beta1
name: vscode-demo
# Optional: deploy a simple pod
deployments:
my-app:
helm:
# If chart: is omitted, component chart will be used
values:
containers:
- image: golang:1.18
# Start development for that pod
dev:
my-app:
# Select the pod we just have deployed
imageSelector: golang:1.18
# Make sure the pod is sleeping
command: ["sh", "-c", "tail -f /dev/null"]
# Change working dir to /app
workingDir: /app
# Create ssh connection to container and save my-app.devspace ssh configuration to ~/.ssh/config
ssh:
localHostname: my-app.devspace
# Forward the port to the local machine
ports:
- port: 9000:9000
# Sync local files into container at /app
sync:
- path: ./:/app
- path: "${DEVSPACE_USER_HOME}/.gitconfig:/root/.gitconfig"
file: true
disableDownload: true
# Optional: make sure git credentials and devspace are available inside the container
proxyCommands:
- gitCredentials: true
- command: devspace
# Define the flow when what is started
pipelines:
dev: |-
# Deploy the application and then start dev
run_default_pipeline dev
# Open VSCode as soon as we are done
code --folder-uri vscode-remote://ssh-remote+my-app.devspace/app
Let's break down the file into what DevSpace will do:
- DevSpace will create a new pod in your specified namespace that runs the
golang:1.18container image - DevSpace will upload its small helper binary into the container and start syncing the source code as well as your
.gitconfiginto the container - Then DevSpace will forward the port
9000from the container to the local machine - Afterwards, DevSpace will start an SSH server inside the container and configure your local ssh config with host
my-app.devspace - Next, DevSpace will create a small git credentials helper script inside the container to make your local git credentials available inside the container as well as allow usage of the local
devspacecommand inside the container - And lastly, DevSpace will open Visual Studio Code inside the container
3. Start DevSpace
Now let's start DevSpace with the following command:
devspace dev -n test
You should see the DevSpace output and then a new VSCode window should open up inside the container. Visual Studio Code will then configure itself. Make sure to install the go extension and the go helper binaries to start the application properly.
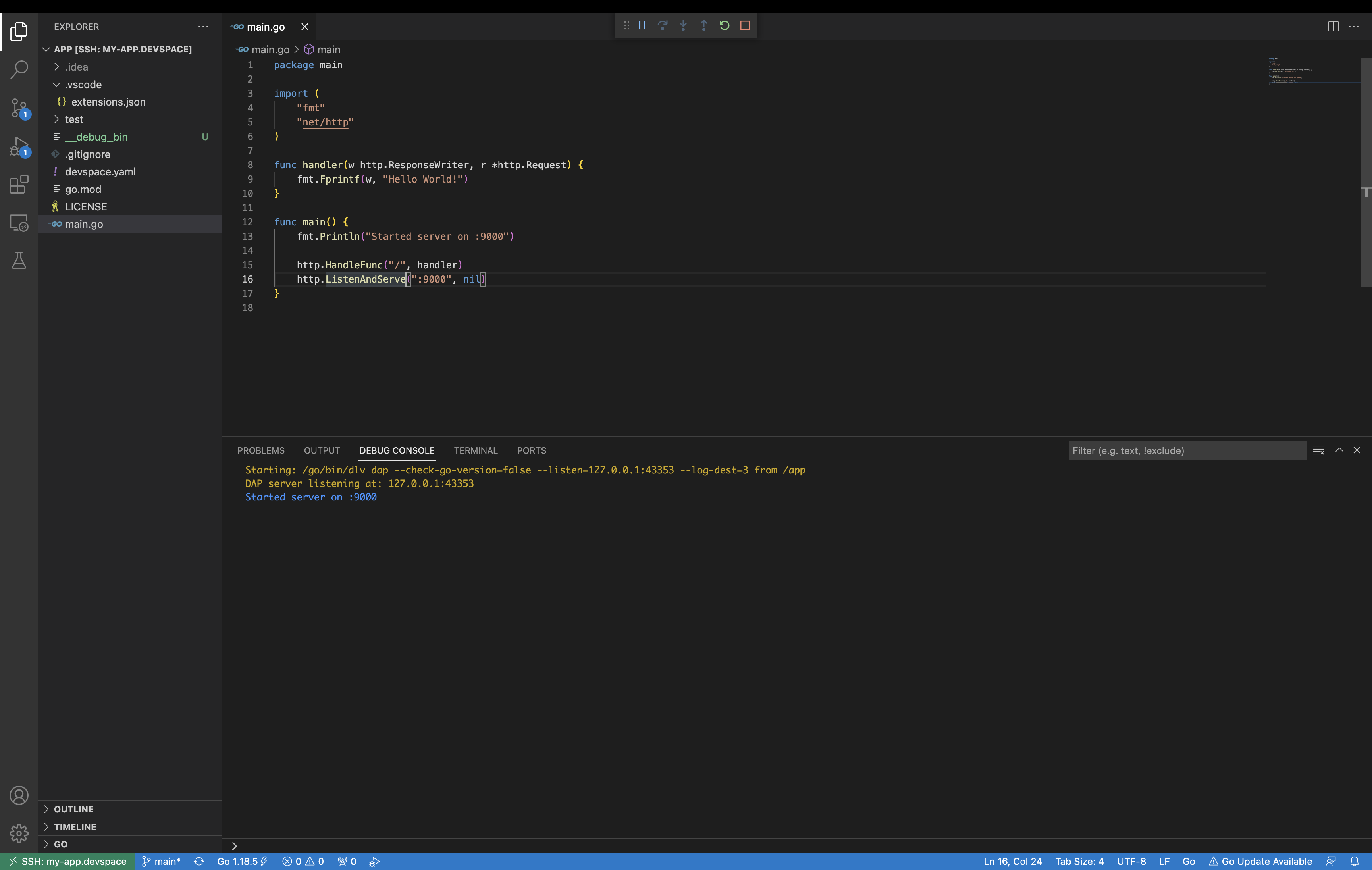
Now navigate to localhost:9000 and you should see the message from our server. Congratulations, you have now used DevSpace to successfully start an application inside Kubernetes with Visual Studio Code.
